Bitcoin Programmability: The Complete Picture

For over a decade, Bitcoin has been framed as digital gold. A static store of value meant to sit in cold storage and appreciate. That narrative captured mainstream attention and drove institutional adoption, but it also constrained how people thought about Bitcoin's potential.
What they didn’t realize then: the design limitations of Bitcoin Script were never permanent barriers. They were technical realities waiting for the right solution.
The conversation is shifting as new infrastructure finally makes it possible to use Bitcoin in ways that were previously out of reach. Bitcoin can do more than store value. It can enforce agreements. It can coordinate counterparties. It can serve as the foundation for economically meaningful activity without sacrificing the security model that made it valuable in the first place.
This is the complete picture of Bitcoin programmability: what it means, how it works, and why it matters now.
From Static Commodity to Programmable Capital
Gold cannot express rules. It cannot enforce conditions. It cannot coordinate complex financial operations. Bitcoin can, but only with the right execution framework.
When Bitcoin is treated as capital infrastructure rather than digital metal, the possibilities expand significantly. Collateral management, structured credit, automated settlement, event-driven conditions, and multiparty coordination all become feasible without stepping outside the base layer. All the mechanics that form an actual economy.
The digital gold narrative served its purpose: It established Bitcoin as the reserve asset institutions trust.
But that framing also limited development. If Bitcoin's only role is passive storage, builders naturally moved to more programmable chains that could deliver more complex financial instruments and, ultimately, greater yield and opportunity generation.
Bitcoin’s next stage requires enabling productive capital. Strategies running onchain. Credit managed with blockspace. Applications coordinating value. All backed by Bitcoin's landmark validation and liquidity.
The Execution Environment Bitcoin Has Been Missing
Bitcoin validates transactions with extraordinary precision, but it was never designed to interpret complex financial logic on its own. For anything more sophisticated than a simple spend, you need a mechanism capable of evaluating conditions, checking rules, and coordinating inputs before transactions touch the UTXO set.
That mechanism is an execution environment. Not a parallel chain, bridge, or metaprotocol layered on top of Bitcoin, but a framework that processes financial operations, checks them against strict rules, and anchors the final result directly to Bitcoin in a format the base layer can independently validate.
This is what the ArchVM does. It is a custom-built VM, based on the eBPF virtual machine that Solana used, but tailor-made with custom syscalls that validate UTXOs and post transactions directly onto Bitcoin.
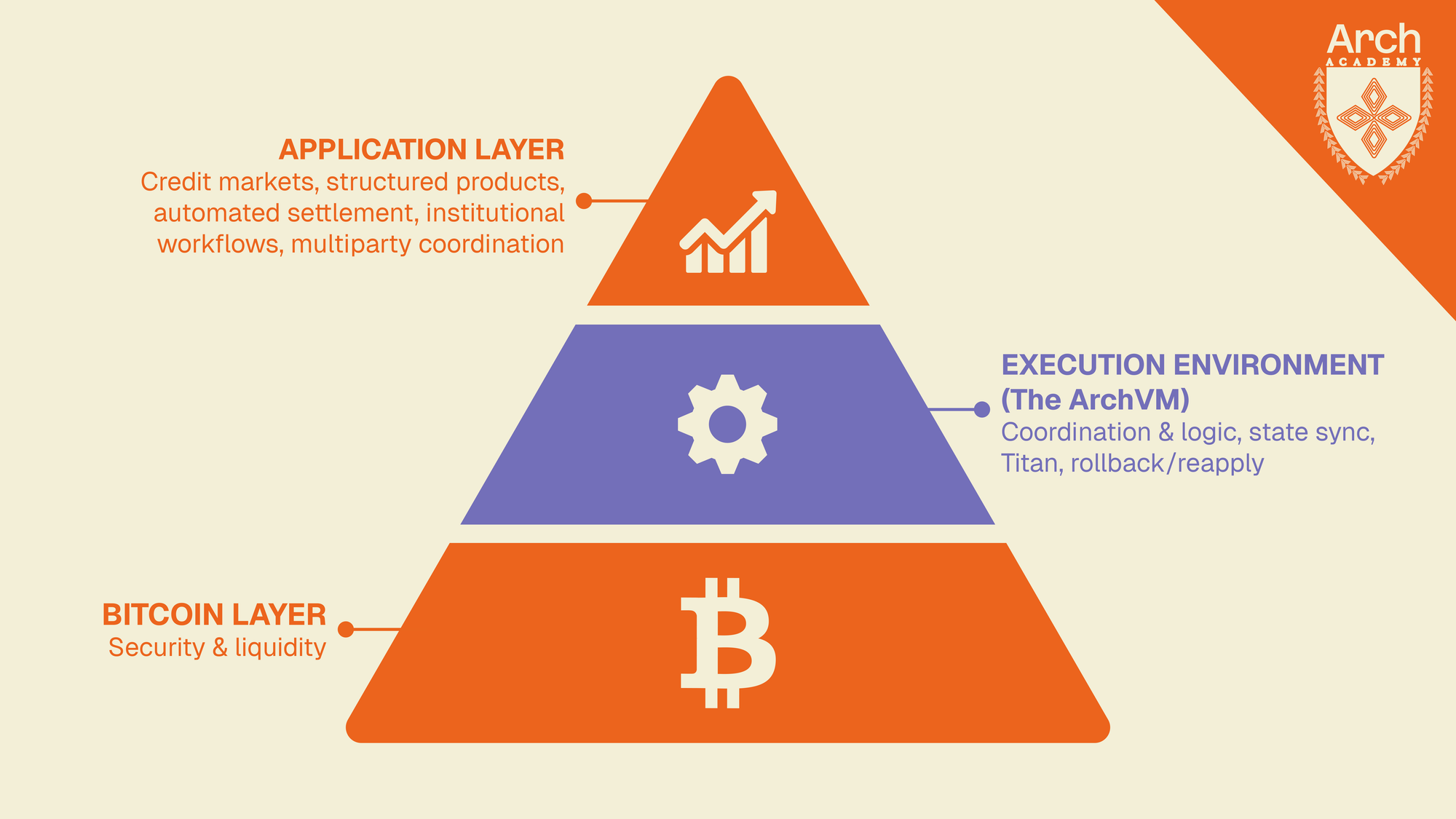
Combined with its unique consensus mechanism, this allows the ArchVM to bring smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin base layer without bridging or wrapping assets: it can evaluate complex financial instructions, enforces constraints, and produces transactions that Bitcoin nodes can verify.
Why This Isn't an L2
The distinction matters. L2s require users to bridge or wrap assets to access greater programmability. They maintain separate state machines that sync back to Bitcoin only when posting commitments or proofs. Their execution and validators exist entirely elsewhere, independent of what's happening on the Bitcoin base layer.
The ArchVM operates differently. The same validators who approve transactions within the ArchVM hold proportional key shares in Arch's FROST+ROAST cryptography on Bitcoin. State changes are reflected accordingly through a real-time mempool indexer (the Titan indexer) and a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) that tracks state transitions on Arch and corresponding asset transfers on Bitcoin to ensure they remain atomic.
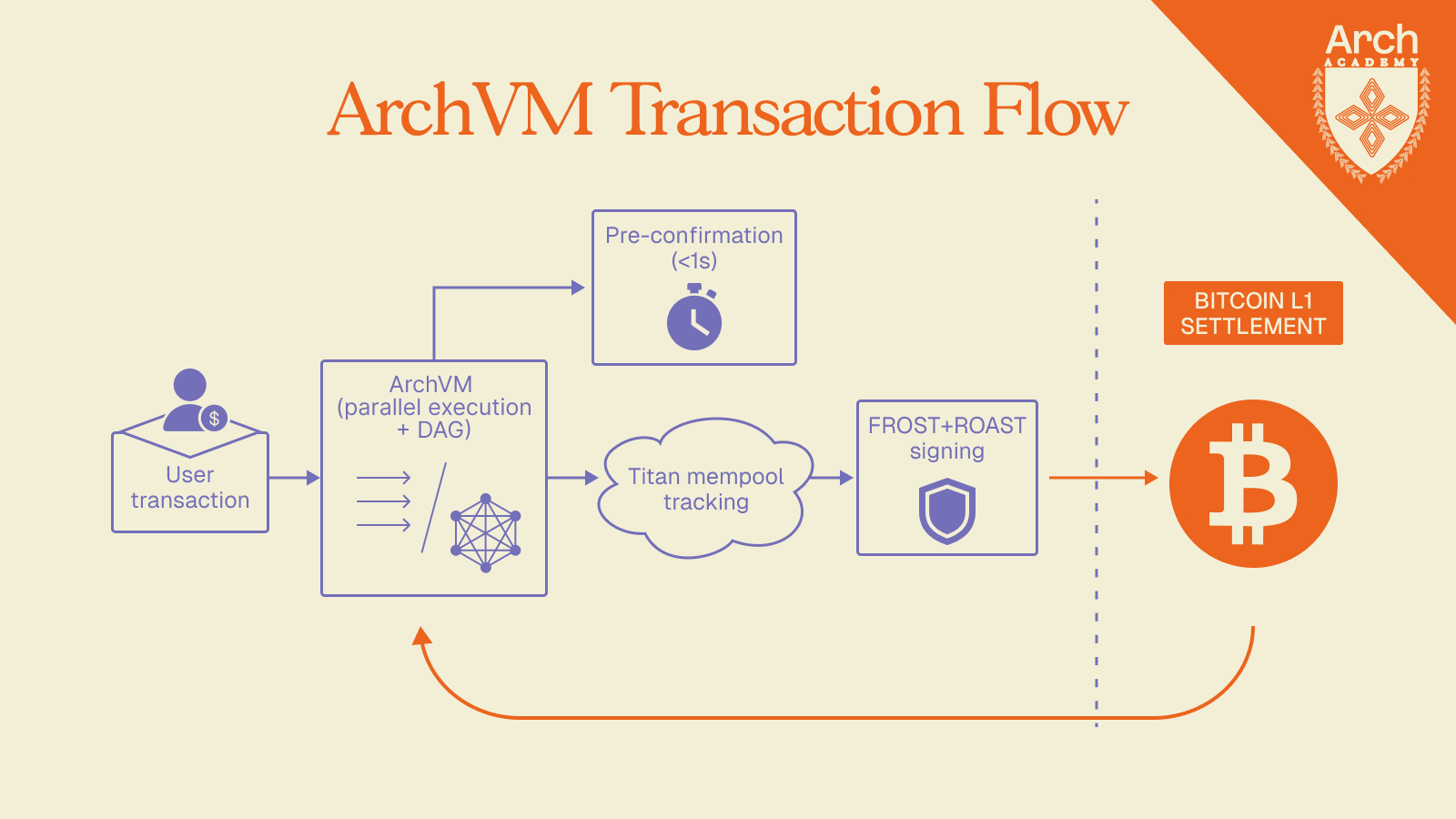
The rollback/reapply mechanism maintains state consistency between Bitcoin's probabilistic finality and Arch's high-performance execution. When Bitcoin transactions fail to confirm due to mempool eviction or reorganizations, the system can surgically roll back only the affected transactions and their dependencies, not entire blocks. When previously failed transactions eventually confirm, they're reapplied in the correct order.
This architecture enables pre-confirmations: transactions can be executed at the Arch level with sub-second responsiveness before final settlement on Bitcoin. Users get near-instant feedback without waiting for Bitcoin's 10-minute block times, while developers can build applications that operate within Bitcoin's security model without introducing the UX friction that has historically plagued Bitcoin DeFi.
Distributed Security Through Decentralized Validators
For financial applications to operate onchain without single points of failure, security must be distributed. No one should be able to push a transaction through independently, and no application should hinge on a coordinator that sits outside Bitcoin's guarantees.
Arch validators participate in both the evaluation and signing of programs processed in the Arch execution environment and ultimately settled as transactions on Bitcoin. The architecture works in stages.
First, the ArchVM takes smart contract instructions communicated via Bitcoin UTXOs and processes them in its faster, more performant environment, allowing it to execute complex transactions without the limitations of Bitcoin Script and Bitcoin’s 10-minute block times. This is critical for enabling a greater Bitcoin economy at scale.
Arch Validators confirm those transactions within the ArchVM and on Bitcoin, through a cutting-edge model, using FROST (Flexible Round-Optimized Schnorr Threshold) combined with ROAST (Robust Asynchronous Schnorr Threshold) signatures.
This requires majority consensus of validators to produce a valid Bitcoin signature. The FROST protocol enables t-of-n threshold signing where only a specified subset needs to cooperate, while ROAST adds robustness by managing multiple concurrent signing sessions. Even if some sessions fail due to malicious actors or network issues, remaining sessions can still produce valid signatures, creating a more stable validation model than consensus models that rely on FROST alone.
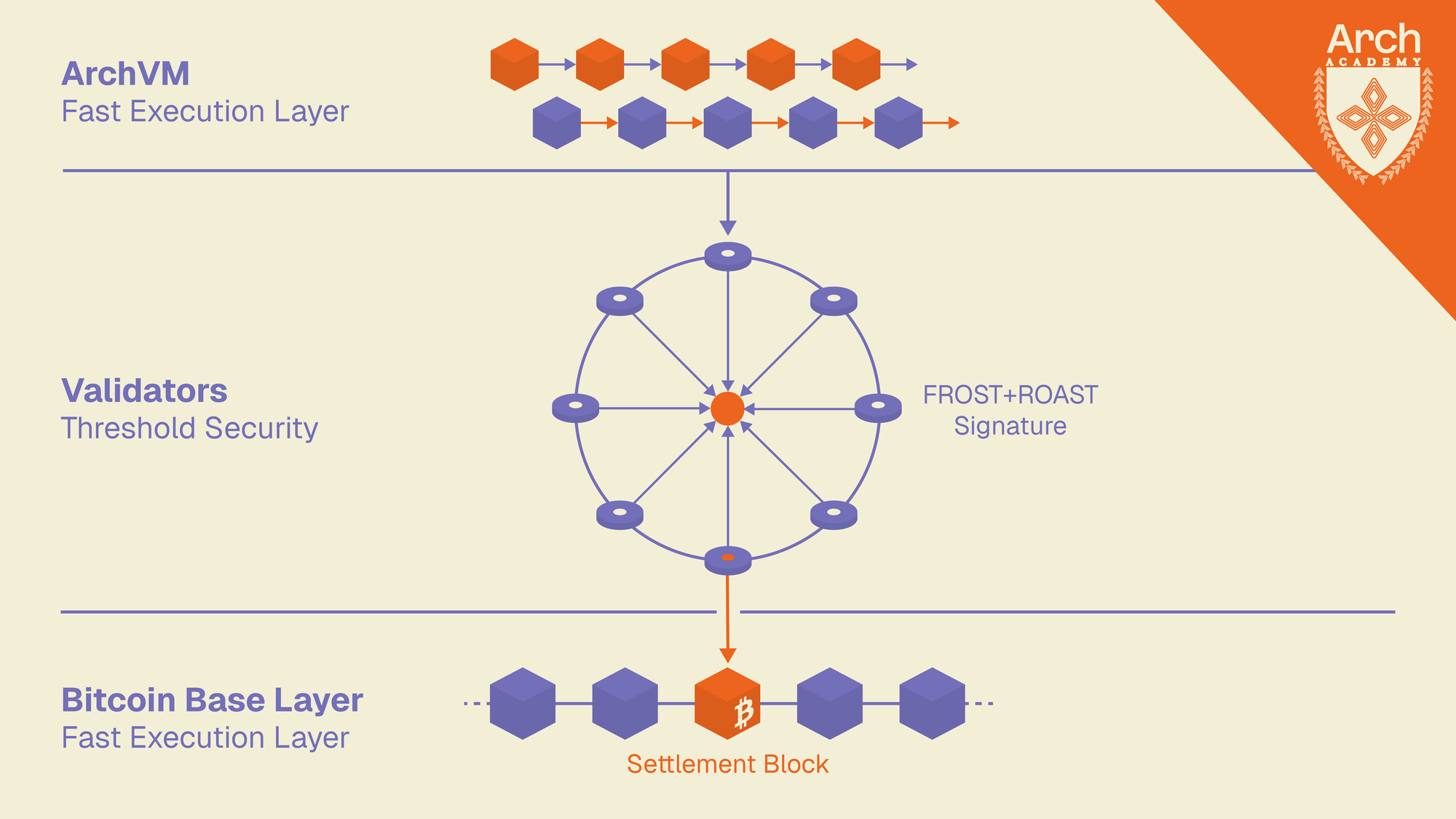
The resulting threshold signature appears externally as a single Schnorr signature but is actually composed of key shares from multiple validators. This signature can control specific Bitcoin addresses, allowing Arch transactions to be simultaneously submitted directly on the Bitcoin network. Once the transaction is included and confirmed in a Bitcoin block, the Arch transaction achieves full settlement finality.
If not accounted for, this could create a state concurrency issue: after all, Bitcoin has 10-minute blocks, while Arch’s are significantly faster. Arch uses its DAG to track dependent transactions, so if a Bitcoin block doesn’t confirm, affected transactions can be rolled back and re-applied accordingly within the Arch state.
This is possible in part due to the custom-built Titan indexer, Bitcoin's only mempool-level indexer, which provides real-time synchronization and security response. Titan tracks all transactions in the Bitcoin mempool before block inclusion, enabling Arch to assess the likelihood that pre-confirmed transactions will actually confirm quickly at L1.
This complex architecture is necessary to create the type of multiparty financial applications that can transform Bitcoin into more than a simple store of value. Credit relationships, coordinated settlements, structured payouts, and conditional actions all require complex programmability and guarantees that no individual participant can alter outcomes. This validator model delivers those guarantees while maintaining the speed and complexity needed for responsive applications.
Building a Bitcoin Economy That Generates Real Fees
The technical infrastructure exists. The security model works. But programmability is only valuable if it enables economically meaningful activity. Activity that people are willing to pay for.
Projects building on Arch illustrate how financial applications function when execution and settlement are coordinated through Bitcoin itself.
Saturn provides AMM-based swaps for Bitcoin-native assets including Runes tokens. Since launching in December 2024, Saturn has processed millions of transactions, establishing itself as a central liquidity hub for early Bitcoin DeFi. The platform offers foundational liquidity pools and ensures interoperability with other dApps through ArchVM's cross-program invocation feature.
Autara Finance is a Bitcoin-native money market built on Arch that allows users to supply BTC and supported assets to earn interest or borrow instantly without bridges or wrapping. With independent risk-isolated pools and configurable oracle stacks, Autara maximizes capital efficiency while driving Bitcoin liquidity inflows.
Bump is a Bitcoin-native token launchpad that enables fast and transparent project launches powered by Arch Network. Built by a team with deep experience in Solana ecosystem and attention-driven consumer apps, Bump lets projects raise capital through a bonding-curve sale. Once the bond completes, the token is automatically minted and paired with liquidity on the Saturn decentralized exchange, giving it instant tradability on Bitcoin rails. Pre- and post- bonding curve, tokens remain fully usable. In the future, Bump V2 will also mint a corresponding Rune to further empower the ecosystem and expand token utility across the Bitcoin ecosystem.
HoneyB focuses on bringing real-world assets onchain. Starting with gold and expanding into private credit, trade finance, and structured products, HoneyB partners with Chintai to deliver institutional-grade infrastructure for issuance, settlement, and compliance. The platform's bridgeless design circulates tokenized assets directly on Bitcoin without wrapped or intermediary structures, positioning Arch as the gateway to multi-trillion-dollar real asset markets.
This activity matters beyond individual applications. Every transaction processed through Arch that settles on Bitcoin generates fees for Bitcoin. As the ecosystem scales, that fee generation becomes increasingly significant, not just for Arch validators, but for Bitcoin miners themselves.
Once all 21 million Bitcoin have been mined, the network will depend entirely on transaction fees for security. If Arch grows to regularly generate substantial transaction volume anchored to Bitcoin, it provides miners with a stable source of fee revenue. In essence, Arch reinforces Bitcoin's long-term sustainability by expanding its utility as a network and ensuring the fee market remains robust enough to incentivize continued mining.
The Complete Picture
Bitcoin programmability builds on the same properties that made Bitcoin the world’s most secure and liquid settlement layer, extending those strengths into broader financial activity beyond basic value transfer.
The ArchVM provides the execution framework Bitcoin needs: Turing-complete computation that works with Bitcoin's constraints rather than fighting them, validator architecture that distributes security across a permissionlessly scalable signer set, and state management mechanisms that handle Bitcoin's probabilistic finality while delivering sub-second user experiences.
Applications using Arch are creating steady financial activity that settles on Bitcoin. Lending, issuance, collateral management, and liquidity operations can now run through programmatic workflows designed to remain aligned with the base layer.
As these systems scale, Bitcoin will function as the settlement foundation for increasingly sophisticated financial operations … with Arch providing the execution environment that links program logic to verifiable onchain outcomes.
The digital gold narrative captured attention. The programmable Bitcoin narrative enables everything that comes next. And those who can see the complete picture will become leaders in making the world's most secure settlement layer the foundation for the new onchain global economy.
For technical details on ArchVM, validator architecture, and the Titan indexer, visit docs.arch.network.
